目录
Math类
查看API文档,可以看到API文档中关于Math类的定义如下:(了解就行)

Math类所在包为java.lang包,因此在使用的时候不需要进行导包。并且Math类被final修饰了,因此该类是不能被继承的。
Math类包含执行基本数字运算的方法,可以使用Math类完成基本的数学运算。
要想使用Math类我们就需要先创建该类的对象,那么创建对象就需要借助于构造方法。因此就需要首先查看一下API文档,看看API文档中针对Math类有没有提供对应的构造方法。通过API文档来查看一下Math类的成员,如下所示:

在API文档中没有体现可用的构造方法,因此就不能直接通过new关键字去创建Math类的对象。同时发现Math类中的方法都是静态的,因此在使用的时候可以直接通过类名去调用。在Math类中定义了很多数学运算的方法。
常见方法
Math的常见方法,都是静态方法
public static int abs(int a) // 返回参数的绝对值
public static double ceil(double a) // 向上取整
public static double floor(double a) // 向下取整
public static int round(float a) // 四舍五入
public static int max(int a,int b) // 获取较大值
public static int min(int a,int b) // 获取较小值
public static double pow (double a,double b) // 计算a的b次幂的值
public static double random() // 返回一个[0.0,1.0)的随机值
演示:
public class MathDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public static int abs(int a) 返回参数的绝对值
System.out.println("-2的绝对值为:" + Math.abs(-2));//-2的绝对值为:2
System.out.println("2的绝对值为:" + Math.abs(2));//2的绝对值为:2
//int 的范围-2147483648~2147483647
//所以abs(-2147483648) 会报错,超出int的正数范围
//在JDK15之后出现absExact(),会先判断是否超出范围再取绝对值
// public static double ceil(double a) 向上取整
System.out.println(Math.ceil(23.45));//24.0
System.out.println(Math.ceil(-23.45));//-23.0
// public static double floor(double a) 向下取整
System.out.println(Math.floor(23.45));//23.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(-23.45));//-24.0
// public static int round(float a) 按照四舍五入返回最接近参数的int
System.out.println("23.45四舍五入的结果为:" + Math.round(23.45));//23
System.out.println("23.55四舍五入的结果为:" + Math.round(23.55));//24
// public static int max(int a,int b) 返回两个int值中的较大值
System.out.println(Math.max(23, 45));//45
// public static int min(int a,int b) 返回两个int值中的较小值
System.out.println(Math.min(12 , 34));//12
// public static double pow (double a,double b)返回a的b次幂的值
System.out.println("2的3次幂计算结果为: " + Math.pow(2,3));//8.0
//如果第二个参数是0~1之间的小数
System.out.println( Math.pow(4,0.5));//2.0
System.out.println( Math.pow(2,-2));//0.25
//一般第二个参数是大于等于1的正整数
//开平方
System.out.println( Math.sqrt(4));//2.0
//开立方
System.out.println( Math.cbrt(8));//2.0
// public static double random()返回值为double的正值,[0.0,1.0)
System.out.println("获取到的0-1之间的随机数为: " + Math.random());
//获取到的0-1之间的随机数为: 0.7322484131745958
System.out.println( Math.floor(Math.random()*100)+1);
//Math.random() [0.0 1.0)
//*100 [0.0 100.0)
//floor 去掉了后面的小数
//+1 [1 100.0]
}
}
算法小题-质数
需求:
判断一个数是否为一个质数
代码实现:
//以前的方法:判断997,依次除以2~996,需要995次,效率太低
public class MathDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断一个数是否为一个质数
System.out.println(isPrime(997));
}
public static boolean isPrime(int number) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(number); i++) {
count++;//循环次数
if (number % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
System.out.println(count);//30
return true;
}
}
算法小题-自幂数
自幂数,一个n位自然数等于自身各个数位上数字的n次幂之和
举例1:三位数 1^3 + 5^3 + 3^3 = 153
举例2:四位数 1^4 + 6^4 + 3^4 + 4^3 = 1634
如果自幂数是:
-
一位自幂数,也叫做:独身数
-
三位自幂数:水仙花数 四位自幂数:四叶玫瑰数
-
五位自幂数:五角星数 六位自幂数:六合数
-
七位自幂数:北斗七星数 八位自幂数:八仙数
-
九位自幂数:九九重阳数 十位自幂数:十全十美数
要求:统计一共有多少个水仙花数
//水仙花数:100 ~ 999
int count = 0;
//得到每一个三位数
for (int i = 100; i <= 999; i++) {
//个位 十位 百位
int ge = i % 10;
int shi = i / 10 % 10;
int bai = i / 100 % 10;
//判断:
//每一位的三次方之和 跟本身 进行比较。
double sum = Math.pow(ge, 3) + Math.pow(shi, 3) + Math.pow(bai, 3);
if (sum == i) {
count++;
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
System类
查看API文档,我们可以看到API文档中关于System类的定义如下:(了解就行)

System类所在包为java.lang包,因此在使用的时候不需要进行导包。并且System类被final修饰了,因此该类是不能被继承的。
System包含了系统操作的一些常用的方法。比如获取当前时间所对应的毫秒值,再比如终止当前JVM等等。
要想使用System类就需要先创建该类的对象,那么创建对象就需要借助于构造方法。因此就需要首先查看一下API文档,看看API文档中针对System类有没有提供对应的构造方法。通过API文档来查看一下System类的成员,如下所示:
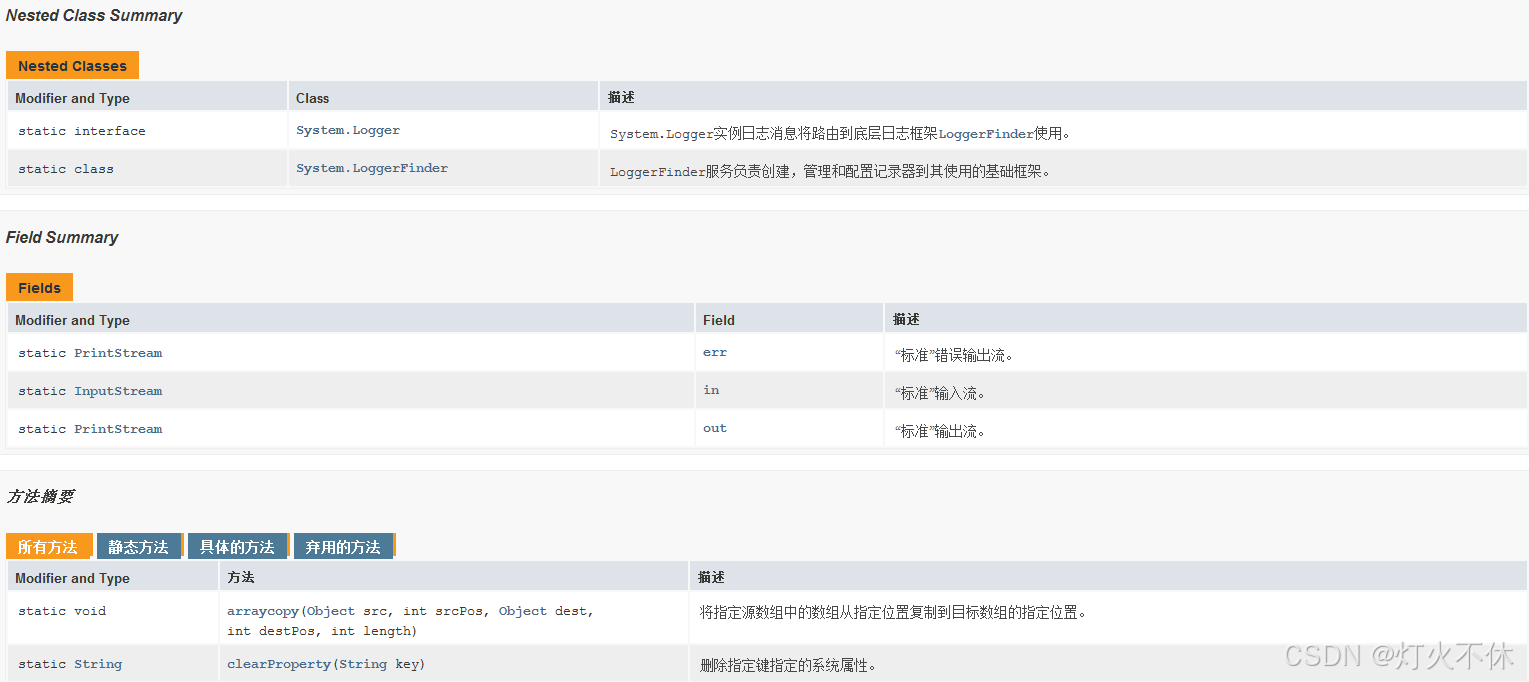
在API文档中没有体现可用的构造方法,因此就不能直接通过new关键字去创建System类的对象。同时我们发现System类中的方法都是静态的,因此在使用的时候可以直接通过类名去调用(Nested Class Summary内部类或者内部接口的描述)。
常见方法
计算机中的时间原点(C语言诞生):1970年1月1日 00:00:00
在中国会有八小时的时差,所以在中国获取操作系统的时间原点为1970年1月1日 08:00:00
- 1秒=1000毫秒
- 1毫秒=1000微秒
- 1微秒=1000纳秒
如下所示:
// 获取当前时间所对应的毫秒值
//(当前时间为0时区所对应的时间即就是英国格林尼治天文台旧址所在位置)
public static long currentTimeMillis()
// 终止当前正在运行的Java虚拟机,0表示正常退出,非零表示异常退出
public static void exit(int status)
// 进行数值元素copy
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos, int length);
案例1:currentTimeMillis方法
//从时间原点开始到运行代码经过了多少时间
public class SystemDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间所对应的毫秒值
long millis = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 输出结果
System.out.println("当前时间所对应的毫秒值为:" + millis);
//当前时间所对应的毫秒值为:1576050298343
}
}
获取到当前时间的毫秒值的意义:常常需要统计某一段代码的执行时间。此时就可以在执行这段代码之前获取一次时间,在执行完毕以后再次获取一次系统时间,然后计算两个时间的差值,
这个差值就是这段代码执行完毕以后所需要的时间。如下代码所示:
public class SystemDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断1~100000之间有多少个质数
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++) {
boolean flag = isPrime2(i);
if (flag) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//获取程序运行的总时间
System.out.println(end - start); //方式一:1514 毫秒 方式二:71毫秒
}
//以前判断是否为质数的方式
public static boolean isPrime1(int number) {
for (int i = 2; i < number; i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
//改进之后判断是否为质数的方式(效率高)
public static boolean isPrime2(int number) {
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(number); i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
案例2:exit方法
//当需要把整个程序结束时使用
public class SystemDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输出
System.out.println("程序开始执行了.....");
// 终止JVM
System.exit(0);
//0:表示当前虚拟机是正常停止
//非0:表示当前虚拟机是异常停止
// 输出
System.out.println("程序终止了..........");
}
}
//程序开始执行了.....
此时可以看到在控制台只输出了"程序开始了...",由于JVM终止了,因此输出"程序终止了..."这段代码没有被执行。
案例3:arraycopy方法
方法参数说明:
// src: 源数组
// srcPos: 源数值的开始索引
// dest: 目标数组
// destPos: 目标数组开始索引
// length: 要复制的元素个数
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
如下所示:
public class SystemDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义源数组
int[] srcArray = {23 , 45 , 67 , 89 , 14 , 56 } ;
// 定义目标数组
int[] desArray = new int[10] ;
// 进行数组元素的copy: 把srcArray数组中从0索引开始的3个元素
//从desArray数组中的1索引开始复制过去
System.arraycopy(srcArray , 0 , desArray , 1 , 3);
// 遍历目标数组
for(int x = 0 ; x < desArray.length ; x++) {
if(x != desArray.length - 1) {
System.out.print(desArray[x] + ", ");
}else {
System.out.println(desArray[x]);
//0, 23, 45, 67, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
}
}
}
}
使用这个方法也可以完成数组元素的删除操作,如下所示:
public class SystemDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个数组
int[] srcArray = {23 , 45 , 67 , 89 , 14 , 56 } ;
// 删除数组中第3个元素(67):要删除67这个元素
//只需要将67后面的其他元素依次向前进行移动即可
System.arraycopy(srcArray , 3 , srcArray , 2 , 3);
// 遍历srcArray数组
for(int x = 0 ; x < srcArray.length ; x++) {
if(x != desArray.length - 1) {
System.out.print(srcArray[x] + ", ");
}else {
System.out.println(srcArray[x]);
//xxxxxxxxxx 23, 45, 89, 14, 56, 56
}
}
}
}
通过控制台输出结果可以看到此时多出了一个56元素,此时只需要将最后一个位置设置为0即可。如下所示:
public class SystemDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个数组
int[] srcArray = {23 , 45 , 67 , 89 , 14 , 56 } ;
// 删除数组中第3个元素(67):要删除67这个元素
//只需要将67后面的其他元素依次向前进行移动即可
System.arraycopy(srcArray , 3 , srcArray , 2 , 3);
// 将最后一个位置的元素设置为0
srcArray[srcArray.length - 1] = 0 ;
// 遍历srcArray数组
for(int x = 0 ; x < srcArray.length ; x++) {
if(x != srcArray.length - 1 ) {
System.out.print(srcArray[x] + ", ");
}else {
System.out.println(srcArray[x]);
//23, 45, 89, 14, 56, 0
}
}
}
}
此时可以看到元素"67"已经被删除掉了。67后面的其他元素依次向前进行移动了一位。
arraycopy方法底层细节:
1.如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是基本数据类型,那么两者的类型必须保持一致,否则会报错
2.在拷贝的时候需要考虑数组的长度,如果超出范围也会报错
3.如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是引用数据类型,那么子类类型可以赋值给父类类型
代码示例:
public class SystemDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan", 23);
Student s2 = new Student("lisi", 24);
Student s3 = new Student("wangwu", 25);
Student[] arr1 = {s1, s2, s3};
Person[] arr2 = new Person[3];
//把arr1中对象的地址值赋值给arr2中
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 3);
//遍历数组arr2
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
Student stu = (Student) arr2[i];
System.out.println(stu.getName() + "," + stu.getAge());
}
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
//get/set方法和构造方法省略
}
class Student extends Person {
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
}
Runtime
Runtime表示当前虚拟机的运行环境,Java中运行时对象,可以获取到程序运行时设计到的一些信息
常见方法
public static Runtime getRuntime() //当前系统的运行环境对象
public void exit(int status) //停止虚拟机
public int availableProcessors() //获得CPU的线程数
public long maxMemory() //JVM能从系统中获取总内存大小(单位byte)
public long totalMemory() //JVM已经从系统中获取总内存大小(单位byte)
public long freeMemory() //JVM剩余内存大小(单位byte)
public Process exec(String command) //运行cmd命令
代码示例:
public class RunTimeDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.获取Runtime的对象,不能用new,因为它的构造方法是私有的
//在类内自己创建了一个对象,可以调用方法获取
//使得在外部获取的是同一个对象
//这个对象代表虚拟机的运行环境,一个电脑只能有一个运行环境,所以只有一个对象
//Runtime r1 =Runtime.getRuntime();
//Runtime r2 =Runtime.getRuntime();
//System.out.println(r1==r2);//true
//2.exit 停止虚拟机
//Runtime.getRuntime().exit(0);
//System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");
//3.获得CPU的线程数
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());//8
//4.总内存大小,单位byte字节
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() / 1024 / 1024);//4064MB
//5.已经获取的总内存大小,单位byte字节
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory() / 1024 / 1024);//254
//6.剩余内存大小
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory() / 1024 / 1024);//251
//7.运行cmd命令
//shutdown :关机
//加上参数才能执行
//-s :默认在1分钟之后关机
//-s -t 指定时间 : 指定关机时间
//-a :取消关机操作
//-r: 关机并重启
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("shutdown -s -t 3600");
//取消关机
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("shutdown -a");
}
}
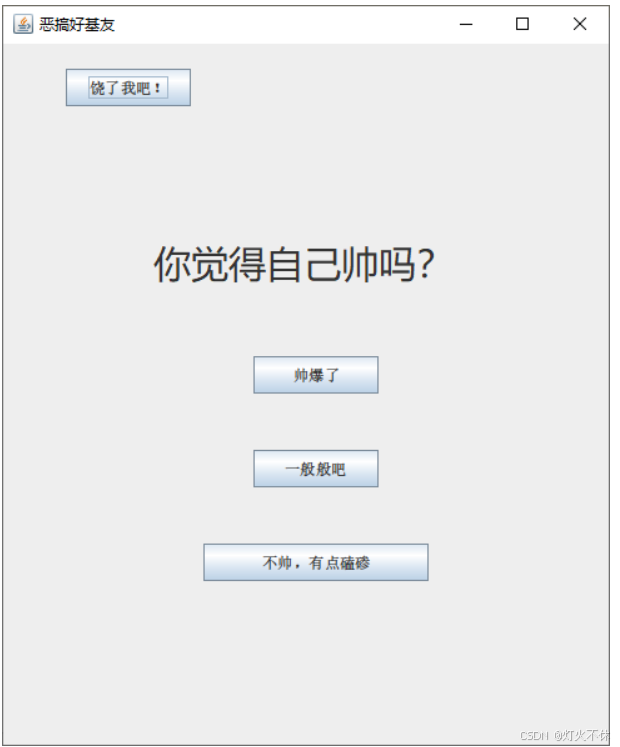
恶搞好基友
需求:
界面上方按钮默认隐藏
界面中间有一个提示文本和三个按钮
当你的好基友点击中间三个按钮的时候就在N秒之后关机,不同的按钮N的值不一样
任意一个按钮被点击之后,上方了按钮出现。当点击上方按钮之后取消关机任务
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyJframe();
}
}
public class MyJframe extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
JButton yesBut = new JButton("帅爆了");
JButton midBut = new JButton("一般般吧");
JButton noBut = new JButton("不帅,有点磕碜");
JButton dadBut = new JButton("饶了我吧!");
//决定了上方的按钮是否展示
boolean flag = false;
public MyJframe() {
initJFrame();
initView();
//显示
this.setVisible(true);
}
private void initView() {
this.getContentPane().removeAll();
if (flag) {
//展示按钮
dadBut.setBounds(50, 20, 100, 30);
dadBut.addActionListener(this);
this.getContentPane().add(dadBut);
}
JLabel text = new JLabel("你觉得自己帅吗?");
text.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", 0, 30));
text.setBounds(120, 150, 300, 50);
yesBut.setBounds(200, 250, 100, 30);
midBut.setBounds(200, 325, 100, 30);
noBut.setBounds(160, 400, 180, 30);
yesBut.addActionListener(this);
midBut.addActionListener(this);
noBut.addActionListener(this);
this.getContentPane().add(text);
this.getContentPane().add(yesBut);
this.getContentPane().add(midBut);
this.getContentPane().add(noBut);
this.getContentPane().repaint();
}
private void initJFrame() {
//设置宽高
this.setSize(500, 600);
//设置标题
this.setTitle("恶搞好基友");
//设置关闭模式
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(3);
//置顶
this.setAlwaysOnTop(true);
//居中
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
//取消内部默认布局
this.setLayout(null);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Object obj = e.getSource();
if (obj == yesBut) {
//给好基友一个弹框
showJDialog("xxx,你太自信了,给你一点小惩罚");
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("shutdown -s -t 3600");
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
flag = true;
initView();
} else if (obj == midBut) {
System.out.println("你的好基友点击了一般般吧");
//给好基友一个弹框
showJDialog("xxx,你还是太自信了,也要给你一点小惩罚");
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("shutdown -s -t 7200");
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
flag = true;
initView();
} else if (obj == noBut) {
System.out.println("你的好基友点击了不帅");
//给好基友一个弹框
showJDialog("xxx,你还是有一点自知之明的,也要给你一点小惩罚");
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("shutdown -s -t 1800");
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
flag = true;
initView();
} else if (obj == dadBut) {
//给好基友一个弹框
showJDialog("xxx,这次就饶了你~");
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("shutdown -a");
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void showJDialog(String content) {
//创建一个弹框对象
JDialog jDialog = new JDialog();
//给弹框设置大小
jDialog.setSize(200, 150);
//让弹框置顶
jDialog.setAlwaysOnTop(true);
//让弹框居中
jDialog.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
//弹框不关闭永远无法操作下面的界面
jDialog.setModal(true);
//创建Jlabel对象管理文字并添加到弹框当中
JLabel warning = new JLabel(content);
warning.setBounds(0, 0, 200, 150);
jDialog.getContentPane().add(warning);
//让弹框展示出来
jDialog.setVisible(true);
}
}